The electric vehicle (EV) revolution in India is in full throttle in 2025, driven by increasing adoption of EVs, government incentives, and growing awareness of environmental sustainability. A key pillar supporting this growth is the rapidly expanding EV charging infrastructure across the country. However, understanding where to charge, the types of chargers available, costs, and charging etiquette is crucial for a smooth EV ownership experience.
This comprehensive guide covers the latest EV charging stations in India, a detailed 2025 map overview, tips for efficient charging, government initiatives, and answers frequently asked questions by EV users.
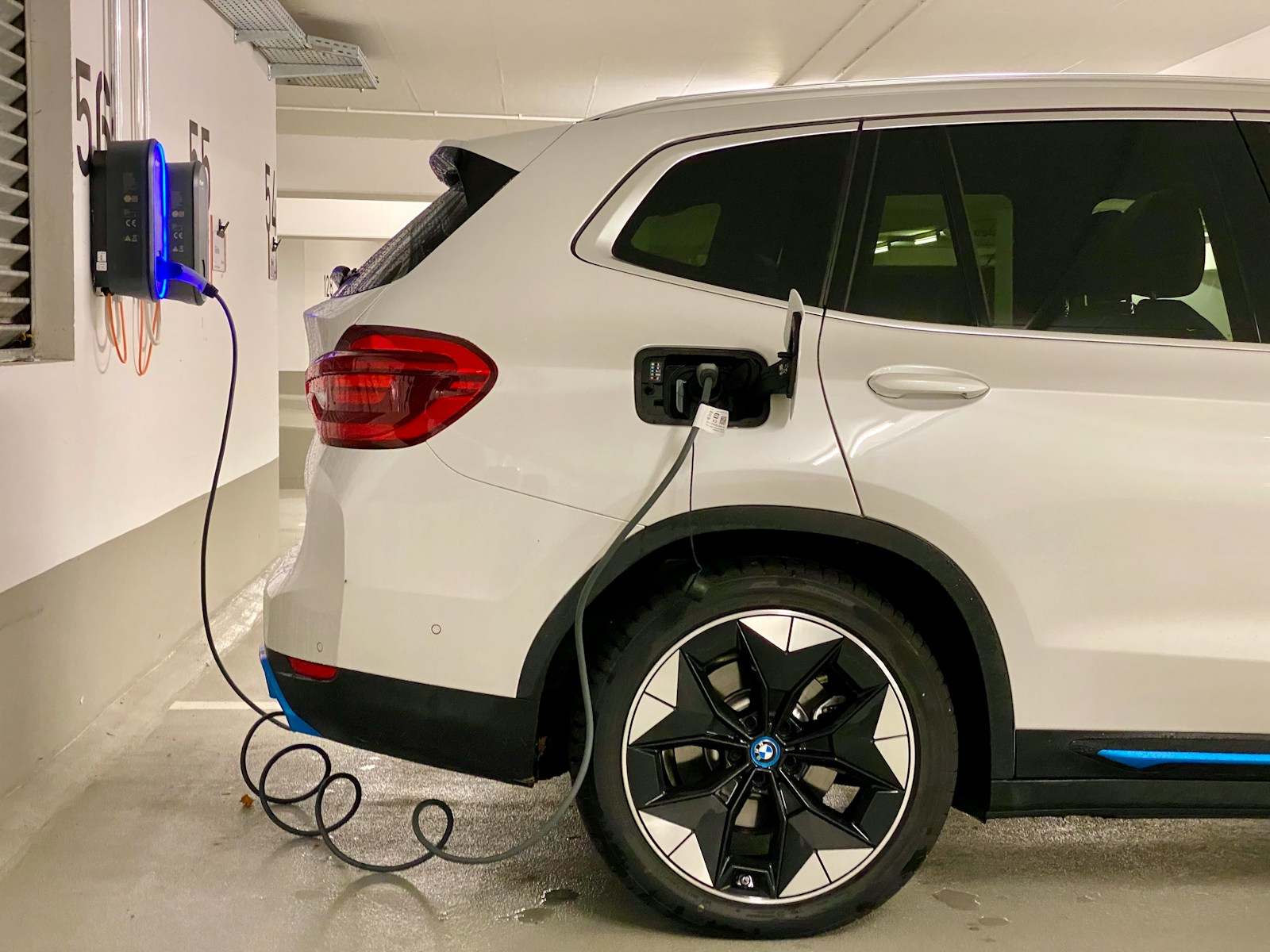

Overview of EV Charging Infrastructure in India
India’s public EV charging network has grown remarkably in recent years. As of early 2025, there are over 26,000 public EV charging stations spread across major urban centers and highways, a 5x increase from just a few years back. This rapid growth results from combined government efforts, private investments by companies like Tata Power, Fortum, Ather Energy, and startups focused on supplementing the infrastructure across Tier 1, 2, and 3 cities.
- The surge follows India’s commitment to national EV adoption targets, with states introducing favorable policies and incentives.
- Despite progress, India currently has roughly one public charger per 235 EVs, highlighting the continued need for infrastructure expansion to keep pace with EV sales [CareEdge Ratings].
Top EV Charging Networks and Their Locations (2025)
| Rank | Charging Network | Key Locations | Types of Chargers | Unique Features | Website / App Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Tata Power EZ Charge | Mumbai, Delhi, Bangalore, Pune, Chennai | AC slow chargers, DC fast chargers | Large network with 5,500+ stations, app support | [Tata Power EZ Charge] |
| 2 | Fortum Charge & Drive | Delhi NCR, Bengaluru, Hyderabad | AC & DC chargers | Scandinavian tech, reliable & fast | [Fortum India EV Charging] |
| 3 | Statiq Charging Network | Pan India – 63+ cities | AC Type 2, DC CCS2 fast chargers | App-based discovery, renewable energy sourced | [Statiq] |
| 4 | Ather Grid | Urban centers primarily (Delhi, Bengaluru, Hyderabad) | Focus on two & four-wheelers, AC chargers | Real-time availability, free charging for some | [Ather Grid] |
| 5 | Jio-BP Pulse | Mumbai, Delhi NCR | Multi-speed DC fast chargers | Combined fuel and EV stations | [Jio-BP Pulse] |
| 6 | Magenta Power ChargeGrid | Navi Mumbai, Maharashtra | Solar-powered, AC & DC chargers | Green energy focus, subscription plans | [Magenta Power] |
| 7 | EVRE | Hyderabad, Telangana | Smart parking + charging combos | B2B & fleet solutions, excellent uptime | [EVRE] |
| 8 | EESL Charging Stations | Government & private fleets across India | Public & fleet chargers | Affordable, government-backed | [EESL EV Charging] |
| 9 | PlugNgo by EV Motors | Gurugram, Haryana | App-based real-time tracking | Corporate & residential focus | [PlugNgo] |
| 10 | ChargeZone | Ahmedabad, Gujarat | High-speed DC chargers | 24/7 operations, highway convenience | [ChargeZone] |
Types of EV Chargers in India
| Charger Type | Power Output | Typical Charging Time* | Best Use Case | Availability in India |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Level 1 (Slow) | 3.3 kW | 8-12 hours (full charge) | Home charging, overnight | Limited public stations |
| Level 2 (AC) | 7-22 kW | 3-7 hours | Home, offices, malls | Widely available |
| DC Fast Charger | 30-120 kW | 30-90 minutes for 80% charge | Highways, quick top-ups | Rapidly expanding network |
| Ultra-Fast Charger | 150+ kW | 15-30 minutes for 80% charge | Long-distance trips, expressways | Emerging (premium locations) |
*Charging time varies depending on battery size and vehicle compatibility.
Expanded Map Highlights (By Region)
- Mumbai & Maharashtra: Tata Power EZ Charge and Magenta Power networks with solar-powered stations.
- Delhi NCR: Fortum Charge & Drive and Jio-BP Pulse lead with fast chargers in commercial centers and highways.
- Bengaluru & Karnataka: Statiq dominates with 7,000+ chargers and expanding renewable energy integration.
- Hyderabad & Telangana: EVRE’s smart infrastructure combined with Tata Power and Ather Grid coverage.
- Ahmedabad & Gujarat: ChargeZone high-speed chargers on highways plus public networks growing.
Public stations are increasingly located in malls, parking lots, petrol stations, IT parks, residential complexes, and highway rest stops for greater accessibility [Statiq][CareEdge Ratings].
Useful Tips for EV Charging Owners in India
- Plan Charging Stops Ahead: Use apps like Tata Power EZ Charge, Statiq, or Fortum to check real-time station availability and plan route accordingly.
- Keep Battery Above 20% Charge Before Reaching Station: Avoid reaching near-complete depletion for battery health and added range flexibility.
- Be Aware of Charger Compatibility: Indian EVs mainly use CCS2 or Type 2 connectors—carry adapters if needed and confirm compatibility.
- Prioritize Fast DC Chargers on Long Trips: Saves time over standard AC chargers especially on highways.
- Avoid Charging in Wet Conditions: Charge only in dry environments to prevent electrical hazards.
- Respect Charging Etiquette: Park only in designated spots, unplug promptly after charging, avoid occupying chargers unnecessarily.
- Utilize Home Charging for Overnight Convenience: Installing a Level 2 home charger provides daily convenience and cost savings.
- Consider Solar-Powered Chargers if Possible: Reduces carbon footprint and future-proofs for clean energy transition [Bolt.Earth][BlinkCharging].
Table: EV Charging Cost Estimates in India (2025)
| Charger Type | Average Cost per kWh (₹) | Estimated Charging Cost (per 30 kWh Battery) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC Home Charger | ₹7 – ₹9 | ₹210 – ₹270 | Depends on home electricity rates |
| Public AC Charger | ₹11 | ₹330 | Slightly higher than home rates |
| DC Fast Charger | ₹15 – ₹18 | ₹450 – ₹540 | Faster, but costlier |
| Ultra-Fast Charger | ₹20+ | ₹600+ | Premium high-speed charging |
FAQs About EV Charging Stations in India
Q1: How many public EV charging stations are currently in India?
As of early 2025, there are around 26,000+ public EV charging stations nationwide, mainly concentrated in metro and Tier 1 cities [CareEdge Ratings].
Q2: Can I charge my EV at home?
Yes, many EV owners install Level 2 chargers at home for overnight charging convenience and cost savings.
Q3: What is the difference between AC and DC chargers?
AC chargers are slower, suitable for home or workplace charging. DC chargers are fast chargers ideal for highways and public stations offering much faster charging times.
Q4: Are EV chargers compatible with all cars?
Most chargers in India use standard connectors like CCS2 or Type 2 compatible with major EVs. However, always check compatibility or carry necessary adapters.
Q5: What is the Telangana EV charging initiative?
Telangana’s EVRE network provides smart parking and charging combos with high uptime and seamless user experience tailored to local needs [EVRE].
Q6: How much does it cost to charge an EV in India?
Costs vary by charger type and location, ranging from ₹7-20 per kWh, translating to ₹200-600 for most mid-sized EV batteries [Tata Power].
External Links & Apps to Locate EV Chargers
- Tata Power EZ Charge App & Map
- Statiq EV Charger Locator
- Fortum Charge & Drive India
- Ather Grid
- PlugNgo by EV Motors
Conclusion
India’s EV charging infrastructure in 2025 shows tremendous growth and promise as the country embraces electric mobility. While the number of charging stations is expanding rapidly, users must remain smart about their charging habits and planning. Leveraging apps, understanding charger types, respecting etiquette, and knowing associated costs enhances the ownership experience and helps overcome range anxiety.
With government backing and private sector thrust, the horizon looks bright for EV infrastructure, making electric vehicle ownership increasingly convenient and accessible throughout India.
Stay charged, drive green, and embrace the EV future with confidence!
Disclaimer: This article is published for general informational purposes based on research, observations, and owner experiences. It should not be considered professional, technical, or legal advice. Vehicle specifications, costs, and procedures may vary by model, location, and time. Readers are advised to verify details with official sources or qualified professionals before making decisions.