How Much Does It Cost to Charge an EV at Home? Complete Guide for Indian EV Owners in 2025

As electric vehicles (EVs) become increasingly popular in India in 2025, one common question from prospective and current EV owners is: How much does it cost to charge an EV at home? Understanding the home charging cost is key to evaluating the total cost of ownership and comparing it to traditional fuel-run vehicles.
This comprehensive guide covers everything EV owners need to know about home charging costs in India, including electricity tariffs, battery sizes and consumption, types of chargers, installation costs, charging efficiency, and tips to reduce your electricity bill.
Understanding EV Home Charging
What is Home Charging?
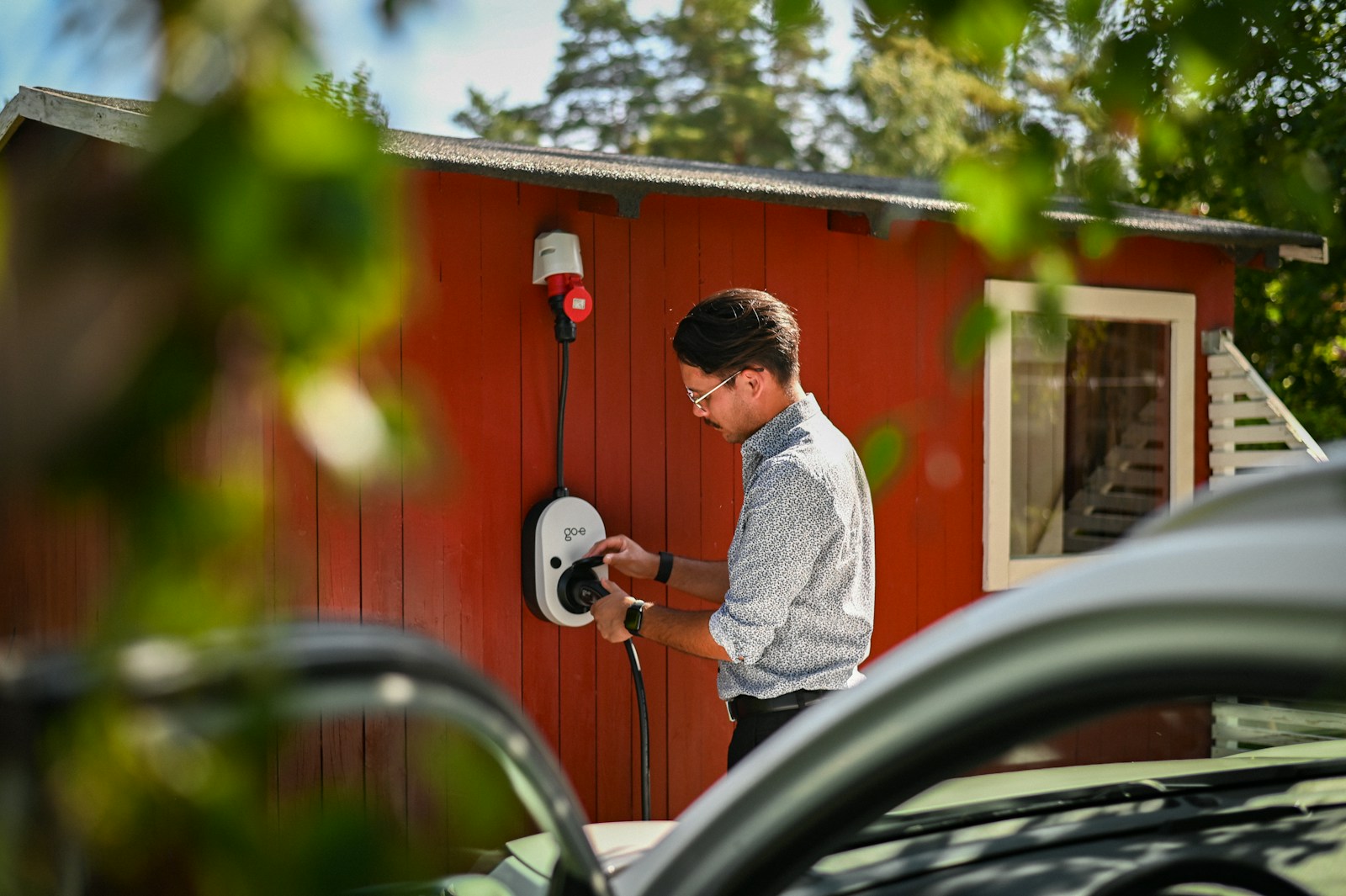
Home charging refers to plugging your electric vehicle into a charging point installed at your residence, typically your garage or parking space. Most home chargers are AC-powered and designed to slowly charge your EV overnight or during downtime.
Home charging provides maximum convenience, savings, and control over when and how you charge your vehicle.
Key Components Affecting Home Charging Cost
1. Electricity Tariff (₹ per kWh)
The primary cost driver is the electricity cost per unit (kilowatt-hour or kWh). This varies widely by state and electricity provider, generally ranging between ₹6 to ₹10 per kWh for residential consumers in India.
Some states offer special EV tariffs or Time of Use (ToU) tariffs reducing rates during off-peak hours, typically at night.
2. Battery Capacity (kWh)
Your EV’s battery capacity in kWh determines how much electricity is needed for a full charge. Small EVs may have battery sizes around 15-20 kWh, while larger models have 40 kWh or more.
3. Charging Efficiency and Losses
Charging efficiency is the ratio of actual energy stored versus electricity drawn from the source. Typical losses of 10-15% occur due to heat and conversion inefficiencies.
4. Charger Type and Power Ratings
- Level 1 Charging: Standard power outlet (slowest — 2-3 kW)
- Level 2 Charging: Dedicated Home AC chargers (7 kW common)
- Level 3/ DC Fast Charging: High power, usually public stations
Higher power chargers reduce charging time but may draw more electricity and involve higher installation costs.
How to Calculate Your EV Charging Cost at Home?
Use this simple formula:Charging Cost=Battery Capacity (kWh)×Electricity Tariff (₹/kWh)×1Charging EfficiencyCharging Cost=Battery Capacity (kWh)×Electricity Tariff (₹/kWh)×Charging Efficiency1
Example:
Tata Nexon EV Long Range with a 40.5 kWh battery
Electricity tariff (Delhi): ₹8 per kWh
Charging efficiency: 85% (0.85)
Charging Cost = 40.5 × 8 ÷ 0.85 ≈ ₹381
This means a full home charge costs approximately ₹380, providing around 450 km range.
Typical Home Charging Costs in Major Indian Cities
| City | Average Residential Tariff (₹/kWh) | Full Charge Cost (for 40 kWh) |
|---|---|---|
| Delhi | 7 – 8 | ₹280 – ₹320 |
| Mumbai | 8 – 10 | ₹320 – ₹400 |
| Bangalore | 6 – 8 | ₹240 – ₹320 |
| Chennai | 5 – 7 | ₹200 – ₹280 |
Note: Costs vary with actual tariff slabs and time of charging.
Installation Cost of Home EV Chargers in India
- Basic wall-mounted AC chargers (Type 2) with 3.3 kW – 7.4 kW: ₹35,000 – ₹70,000
- Installation and wiring costs can add ₹5,000 – ₹15,000 depending on home complexity
- Smart chargers with network capability cost more but offer scheduling and rate optimization
- Subsidies and incentives for charger installation may apply in some states
More info: ICICI Lombard – EV Charger Installation Cost
Comparing Home Charging With Public Charging Costs
| Charging Type | Cost per kWh (₹) | Approximate Cost for Full Charge (₹) |
|---|---|---|
| Home Off-Peak (night) | 6 – 7 | 240 – 280 |
| Home Peak Hours | 9 – 10 | 360 – 400 |
| Public AC (22 kW) | 10 – 14 | 400 – 560 |
| Public DC Fast Charging | 18 – 22 | 720 – 880 |
Home charging is significantly cheaper, particularly when scheduled during off-peak hours.
Saving Tips: How to Reduce Your Home EV Charging Costs
- Install a smart charger to schedule charging during off-peak hours with lower electricity rates.
- Negotiate with your electricity provider or switch to EV-specific tariff plans if available.
- Use solar power to offset charging costs; install rooftop solar if possible.
- Maintain your EV battery well to optimize charging efficiency and range.
- Monitor electricity usage and avoid charging during expensive peak tariff hours.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: Can I charge my EV with a normal home socket?
Yes, but it will be slow (Level 1 charging: 2-3 kW) and may take 8-12 hours or more for a full charge.
Q2: How long does home charging take?
Depends on charger power: Level 2 (7kW) takes 4-6 hours for a full charge typically.
Q3: Is it safe to install EV chargers at home?
Yes, professional installation ensures safety, and EV chargers come with multiple protective systems.
Q4: Do all states have the same electricity tariffs for home charging?
No, tariffs vary state-wise and by electricity board; check local rates for precise cost calculation.
Q5: What is the approximate running cost per km for EVs charged at home?
Typically, ₹0.60 to ₹1 per km, significantly cheaper than petrol or diesel vehicle running costs.
External Resources for EV Home Charging Costs and Details
- Pulse Energy EV Charging Rates
- NorthFleet: EV Charging Cost in India
- Govt of India e-AMRIT Home Charging Calculator
- CarDekho: EV Charging Station Cost
- ISIE India: EV Charging Cost Comparison
Conclusion
Charging an electric vehicle at home in India in 2025 is generally cost-effective, convenient, and environmentally friendly. With average electricity tariffs between ₹6 to ₹10 per kWh, a full recharge typically costs between ₹200 and ₹400 depending on the battery size and location. When compared to public charging stations, home charging is markedly cheaper, especially when scheduled during off-peak hours.
Understanding the factors influencing your home charging cost—such as electricity tariff, battery capacity, and charger type—empowers you to optimize usage and reduce expenses. Furthermore, investing in smart charging infrastructure at home can bring long-term savings and make your EV ownership even more rewarding.
Disclaimer: This article is published for general informational purposes based on research, observations, and owner experiences. It should not be considered professional, technical, or legal advice. Vehicle specifications, costs, and procedures may vary by model, location, and time. Readers are advised to verify details with official sources or qualified professionals before making decisions.